ultimate guide to Sustainable Graphic Design
- yadigitalukltd
- March 2, 2024
- logo design
- sustainable graphic design
- 0 Comments
I. Introduction
Sustainable graphic design focuses on minimizing the environmental impact of visual communication by integrating eco-friendly practices and materials. Its importance is crucial in today’s world due to increasing environmental awareness. By reducing waste, energy consumption, and adopting responsible choices, sustainable graphic design aligns with a global shift towards eco-conscious practices. Businesses benefit by enhancing their brand reputation, attracting environmentally aware consumers, and contributing to a more sustainable future.
I. What is Sustainable Graphic Design?
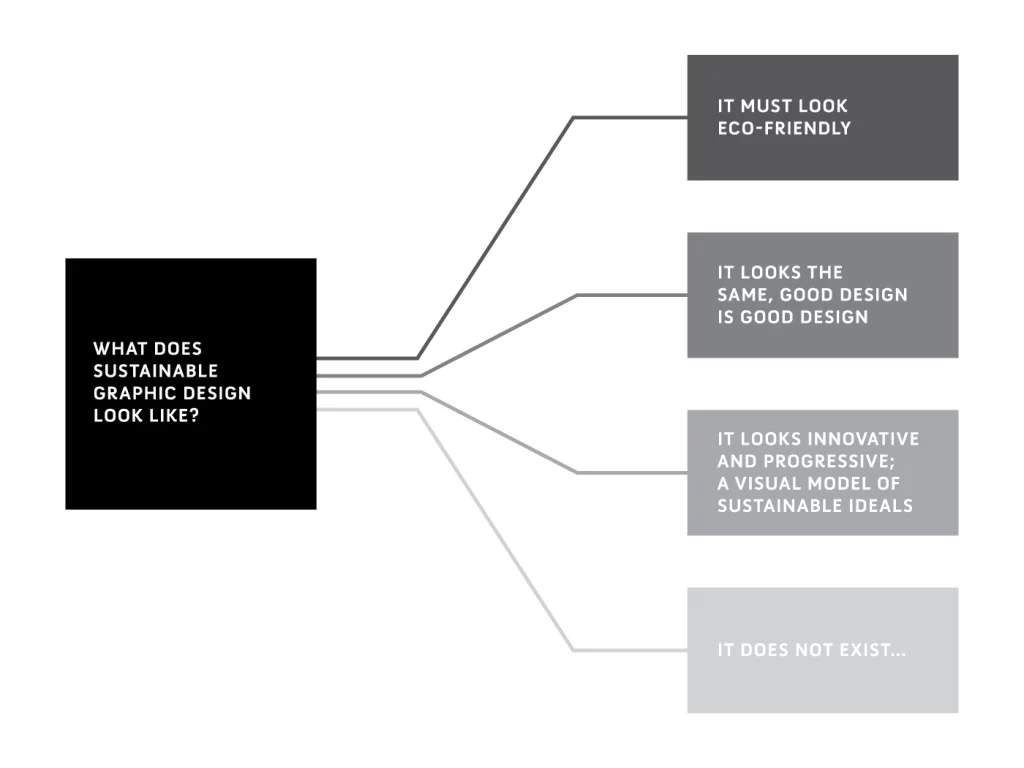
Sustainable graphic design goes beyond merely using eco-friendly materials; it encompasses a holistic approach that considers environmental, social, and economic impacts. Here’s an exploration of the different aspects of sustainable graphic design:
- Environmental Impact:
- Material Choices: Selecting eco-friendly and recyclable materials is a fundamental aspect. Designers can opt for recycled paper, vegetable-based inks, and other sustainable alternatives to traditional graphic design materials.
- Production Methods: Embracing low-impact production processes reduces energy consumption and waste. Techniques like digital printing, which often generate fewer emissions than traditional methods, can be considered.
- Energy Use: Employing energy-efficient technologies and practices, such as using renewable energy sources in the design process, helps minimize the carbon footprint.
- Social Impact:
- Fair Labor Practices: Ensuring that the production of graphic designs adheres to fair labour practices is crucial. This involves working with suppliers and manufacturers that prioritize ethical working conditions and fair wages for employees.
- Representation: Sustainable graphic design should also consider diversity and inclusion. Representing various cultures, genders, and perspectives in designs helps create a positive social impact.
- Economic Impact:
- Lifecycle of Designs: Designing with longevity in mind reduces the need for constant reprints or updates, thereby minimizing waste. Timeless designs contribute to a more sustainable economic model.
- Responsible Sourcing: Opting for responsibly sourced materials ensures that the entire supply chain, from raw materials to production, adheres to ethical and sustainable practices.
- Challenges in Defining Sustainable Graphic Design:
- Subjectivity: The concept of sustainability can be subjective and context-dependent. What may be considered sustainable in one region or industry might not apply universally. Balancing different aspects of sustainability, such as environmental and social considerations, can be challenging.
- Continuous Improvement: The field is dynamic, and what is considered sustainable today might be outdated tomorrow. Designers face the challenge of staying informed about the latest developments in sustainable practices and materials.
Why Do We Need Sustainable Graphic Design?

Sustainable graphic design is crucial for several reasons, as it addresses environmental, social, and economic concerns associated with the design industry. Here are key reasons why we need sustainable graphic design:
- Environmental Impact: Traditional graphic design processes often involve the use of harmful materials, excessive energy consumption, and high levels of waste. Sustainable graphic design aims to minimize these negative environmental impacts by promoting eco-friendly materials, responsible production methods, and waste reduction.
- Resource Conservation: The production of graphic design materials often requires significant amounts of resources, including paper, ink, and energy. Sustainable graphic design emphasizes resource conservation by encouraging the use of recycled and responsibly sourced materials, as well as the adoption of energy-efficient technologies.
- Reducing Carbon Footprint: The carbon footprint of graphic design activities, such as printing and transportation, contributes to climate change. Sustainable graphic design seeks to minimize carbon emissions through practices like using digital media, reducing the need for physical printing, and choosing local suppliers to decrease transportation-related emissions.
- Promoting Ethical Practices: Sustainable graphic design extends beyond environmental concerns to encompass ethical considerations. This includes fair labor practices, ensuring that workers involved in the production of graphic materials are treated ethically and paid fair wages.
- Longevity and Timelessness: Sustainable graphic design encourages the creation of timeless and enduring designs. This contrasts with the fast-paced, trend-driven nature of some design practices that lead to frequent rebranding and disposal of outdated materials. Designing for longevity reduces the need for constant updates and minimizes waste.
- Educating and Raising Awareness: Sustainable graphic design involves educating designers, clients, and the public about the environmental and social impacts of design choices. By raising awareness, the industry can promote responsible decision-making and foster a culture of sustainability.
- Meeting Consumer Expectations: With increasing environmental awareness among consumers, there is a growing demand for sustainable products and services. Embracing sustainable graphic design allows businesses to align with consumer values, potentially attracting a broader audience and enhancing brand reputation.
- Compliance with Regulations: Governments and regulatory bodies are increasingly implementing environmental standards and regulations. Adhering to sustainable graphic design practices ensures that designers and businesses stay compliant with these evolving regulations, avoiding legal and reputational risks.
II. How to Achieve Sustainable Graphic Design

- Use Recycled Materials and Eco-Friendly Inks:
- Recycled Materials: Incorporate recycled paper and other sustainable materials into your design projects. This reduces the demand for new resources and minimizes the environmental impact of production.
- Eco-Friendly Inks: Choose inks that are environmentally friendly, such as those made from soy or vegetable oil rather than traditional petroleum-based inks. These alternatives are biodegradable and have lower VOC (volatile organic compounds) emissions.
- Prioritize Digital Distribution Over Physical Prints:
- Embrace Digital Platforms: Opt for digital distribution channels, such as email newsletters, social media, and online portfolios. This reduces the need for physical prints, cutting down on paper consumption, energy, and transportation-related emissions.
- Interactive Media: Explore interactive and digital media formats that allow for engaging and immersive experiences without the need for excessive printed materials.
- Consider the Lifecycle of Designs:
- Design Longevity: Create designs with a timeless quality, avoiding trends that quickly become obsolete. This approach minimizes the need for frequent redesigns and reprints.
- Adaptability: Design with adaptability in mind, making it easy to repurpose or scale your work for various applications and platforms.
- Proper Disposal Methods:
- Environmental Education: Familiarize yourself with proper disposal methods for design materials, especially physical prints and packaging. This includes recycling paper and other materials and avoiding contamination.
- Encourage Responsible Disposal: Advocate for responsible disposal practices among clients and collaborators. Provide information on recycling programs and facilities for design-related materials.
- Partner with Sustainable Businesses and Organizations:
- Collaborative Impact: Collaborate with businesses and organizations that share a commitment to sustainability. This extends the positive impact of your work throughout the supply chain.
- Supply Chain Considerations: Choose suppliers and manufacturers who adhere to sustainable practices. This ensures that the entire lifecycle of your design, from production to disposal, aligns with eco-friendly principles.
- Reduce Energy Consumption:
- Optimize Software and Devices: Optimize your design software and computer settings to reduce energy consumption. Regularly update your tools to take advantage of energy-efficient features.
- Renewable Energy: Consider using devices powered by renewable energy sources. Additionally, support and advocate for initiatives that promote the use of renewable energy in the design industry.
- Minimize Travel and Shipping Impact:
- Virtual Communication: Utilize virtual communication tools to reduce the need for physical travel. This minimizes your carbon footprint associated with commuting and business-related trips.
- Local Printing: When physical prints are necessary, choose local printing services to minimize shipping distances. This reduces the environmental impact associated with transportation.
- Educate Clients and Peers:
- Advocacy: Actively advocate for sustainable graphic design practices within your professional network. Share information and resources to raise awareness about the environmental impact of design choices.
- Client Education: Educate clients about the environmental benefits of sustainable design. Encourage them to adopt eco-friendly options and consider the long-term impact of design decisions.
- Stay Informed and Evolve:
- Continuous Learning: Stay informed about the latest advancements in sustainable design practices. Attend workshops, webinars, and industry events to stay updated on emerging technologies and methodologies.
- Adaptability: Be open to adopting new technologies and methods that reduce environmental impact. Embrace innovations that contribute to the sustainability of the graphic design industry.
By incorporating these comprehensive strategies into your graphic design workflow, you can actively contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally conscious design practice.

III. The Future of Sustainable Graphic Design
The future of sustainable graphic design holds great promise, as the industry increasingly recognizes the importance of environmental and social responsibility. Several key trends and potential impacts on the industry can be identified:
- Materials Innovation: Sustainable graphic design will likely see a shift towards eco-friendly materials. Designers may explore alternatives to traditional paper and printing methods, such as recycled or tree-free papers, vegetable-based inks, and biodegradable packaging. This shift can significantly reduce the ecological footprint of printed materials.
- Digital Dominance: With the ongoing digital transformation, there is a growing emphasis on digital media and virtual experiences. This shift can lead to reduced reliance on printed materials, thereby minimizing waste and resource consumption. Designers may increasingly focus on creating engaging and impactful digital content.
- Life Cycle Assessment Integration: The integration of life cycle assessments (LCAs) into the design process will become more commonplace. Designers may assess the environmental impact of their creations from production to disposal, considering factors like energy use, material sourcing, and end-of-life considerations. This holistic approach will guide designers in making more sustainable choices.
- Collaboration for Sustainability: Collaboration among stakeholders in the design industry will become crucial. Designers, printers, manufacturers, and clients may work together to implement sustainable practices throughout the supply chain. This collaborative approach can lead to shared resources, knowledge, and technologies, fostering a more sustainable ecosystem.
- Educational Initiatives: The future will likely witness increased emphasis on education and awareness within the graphic design community. Designers may seek to enhance their understanding of sustainable practices and incorporate them into their work. Educational programs and certifications focusing on sustainable design may become more prevalent.
Ethical consideration and challenges
- Greenwashing: There is a risk of greenwashing, where companies may falsely claim to be sustainable for marketing purposes. Designers will need to navigate through such challenges by verifying the authenticity of eco-friendly claims and ensuring that their work genuinely aligns with sustainability goals.
- Cost Considerations: Sustainable materials and processes may, at times, be more expensive than conventional ones. Designers will need to find a balance between sustainability and budget constraints, potentially requiring clients and businesses to recognize the long-term benefits of environmentally friendly practices.
- Consumer Awareness: Educating consumers about the importance of sustainable design and encouraging them to make environmentally conscious choices is crucial. Designers may face the challenge of bridging the gap between sustainable practices and consumer expectations, requiring effective communication and transparency.
- Technological Advancements: Keeping up with rapidly evolving technologies and materials in the sustainable design space can be challenging. Designers will need to stay informed about the latest developments to incorporate cutting-edge, eco-friendly solutions into their work.
the future of sustainable graphic design holds the potential for positive transformation within the industry. Designers, businesses, and consumers alike will play integral roles in shaping a more environmentally and socially responsible design landscape.
“Perfection is achieved, not when there is nothing more to add, but when there is nothing left to take away.” – Antoine de Saint-Exupéry
Conclusion:
In summary, sustainable graphic design is a crucial approach that integrates environmental and ethical considerations into the creative process. By focusing on eco-friendly materials, responsible production methods, and conscious design choices, designers can contribute to a more sustainable future. Key takeaways include the importance of reducing waste, utilizing renewable resources, and prioritizing ethical sourcing.
As designers, we have the power to influence change through our work. Embracing sustainable practices not only aligns with global environmental goals but also promotes responsible consumption and production. By incorporating these principles, we can create designs that leave a positive impact on both our clients and the planet.
To delve deeper into sustainable graphic design, consider further research on innovative eco-friendly materials, staying updated on industry best practices, and collaborating with like-minded professionals. Let’s collectively commit to making conscious choices in our design processes and inspire others to do the same. Together, we can shape a design industry that not only thrives creatively but also contributes to a sustainable and ethical future.
FAQ:
- What is sustainability in graphic design?
- Refers to minimizing environmental and social impacts in the creation of visual communication materials.
- What is the sustainable graphic design process?
- Involves research, eco-friendly material selection, energy efficiency, waste reduction, sustainable printing, and designing for longevity.
- What is sustainable design?
- In graphic design, it’s the creation of visuals with minimal negative impact on the environment, society, and economy.
- What are the 4 common features of sustainable design?
- Environmental considerations, social responsibility, economic viability, and life cycle thinking.
- What are the basic concepts of sustainable design?
- Holistic approach, circular economy, minimization of environmental impact, and social equity.
- What are some examples of sustainable design?
- Eco-friendly packaging, digital design solutions, energy-efficient printing, reusable branding elements, and sustainable typography.